Overview
What is gnet?
gnet is an event-driven networking framework that is ultra-fast and lightweight. It is built from scratch by exploiting epoll and kqueue and it can achieve much higher performance with lower memory consumption than Go net in many specific scenarios.
gnet and net don't share the same philosophy about network programming. Thus, building network applications with gnet can be significantly different from building them with net, and the philosophies can't be harmonized. There are other similar products written in other programming languages in the community, such as libevent, libuv, netty, twisted, tornado, etc. which work in a similar pattern as gnet under the hood.
gnet is not designed to displace the Go net, but to create an alternative in the Go ecosystem for building performance-sensitive network services. As a result of which, gnet is not as comprehensive as Go net, it provides only the core functionalities (in a concise API set) required by a network application and it is not planned on being a coverall networking framework, as I think net has done a good enough job in that area.
gnet sells itself as a high-performance, lightweight, non-blocking, event-driven networking framework written in pure Go which works on the transport layer with TCP/UDP protocols and Unix Domain Socket. It enables developers to implement their own protocols(HTTP, RPC, WebSocket, Redis, etc.) of application layer upon gnet for building diversified network services. For instance, you get an HTTP Server if you implement HTTP protocol upon gnet while you have a Redis Server done with the implementation of Redis protocol upon gnet and so on.
gnet derives from the project: evio while having a much higher performance and more features.
Features
- High-performance event-driven looping based on a networking model of multiple threads/goroutines
- Built-in goroutine pool powered by the library ants
- Lock-free during the entire runtime
- Concise and easy-to-use APIs
- Efficient, reusable, and elastic memory buffer: (Elastic-)Ring-Buffer, Linked-List-Buffer and Elastic-Mixed-Buffer
- Multiple protocols/IPC mechanisms:
TCP,UDP, andUnix Domain Socket - Multiple load-balancing algorithms:
Round-Robin,Source-Addr-Hash, andLeast-Connections - Two event-driven mechanisms:
epollon Linux andkqueueon FreeBSD/DragonFly/Darwin - Flexible ticker event
- Implementation of
gnetClient - Windows platform support (For compatibility in development only, do not use it in production)
- Multiple network addresses binding
- TLS support
- io_uring support
Architecture
Networking Model of Multiple Threads/Goroutines
Multiple Reactors
gnet redesigns and implements a new built-in networking model of multiple threads/goroutines: 『multiple reactors』 which is also the default networking model of multiple threads in netty, Here's the schematic diagram:
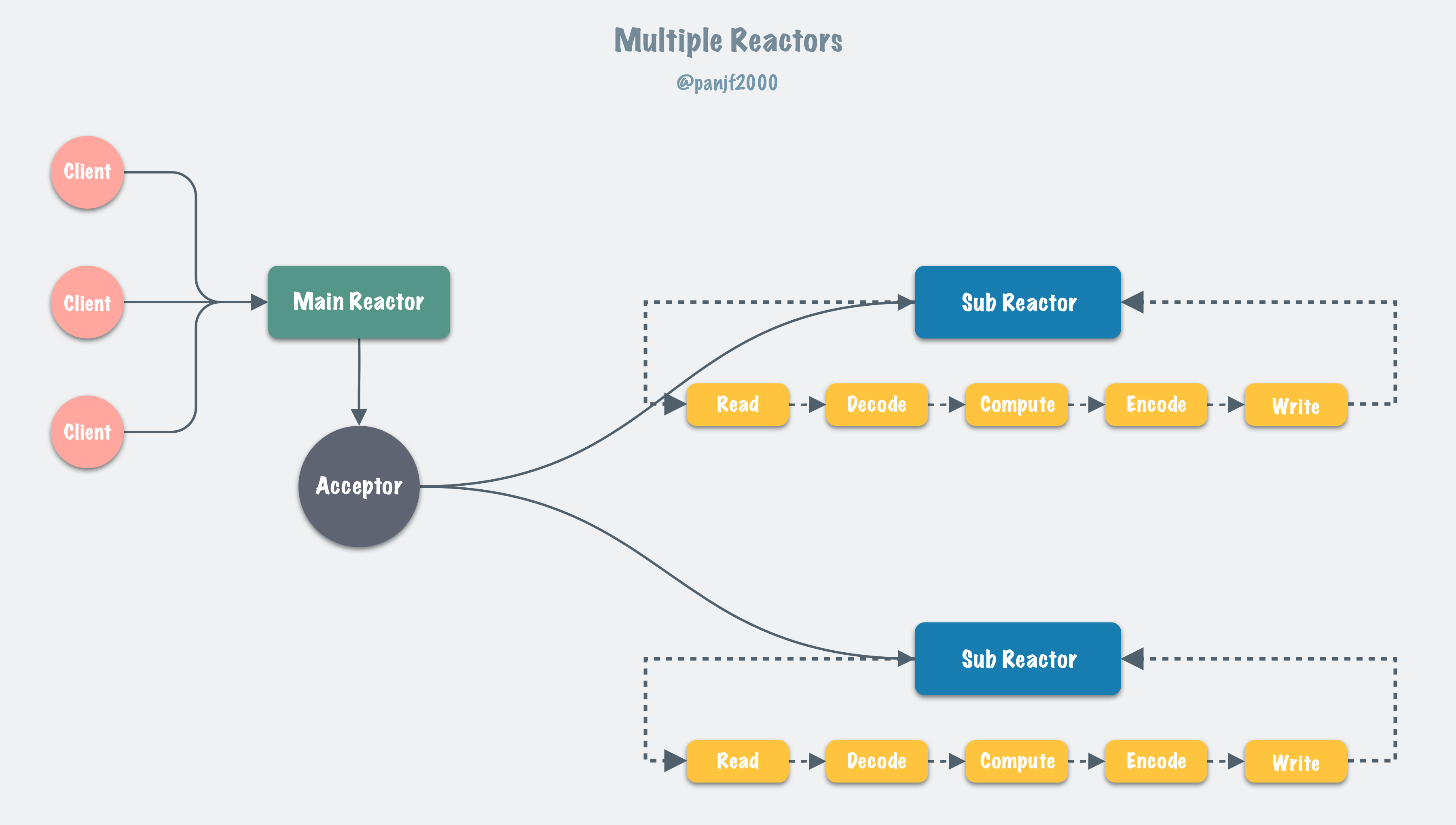
and it works as the following sequence diagram:
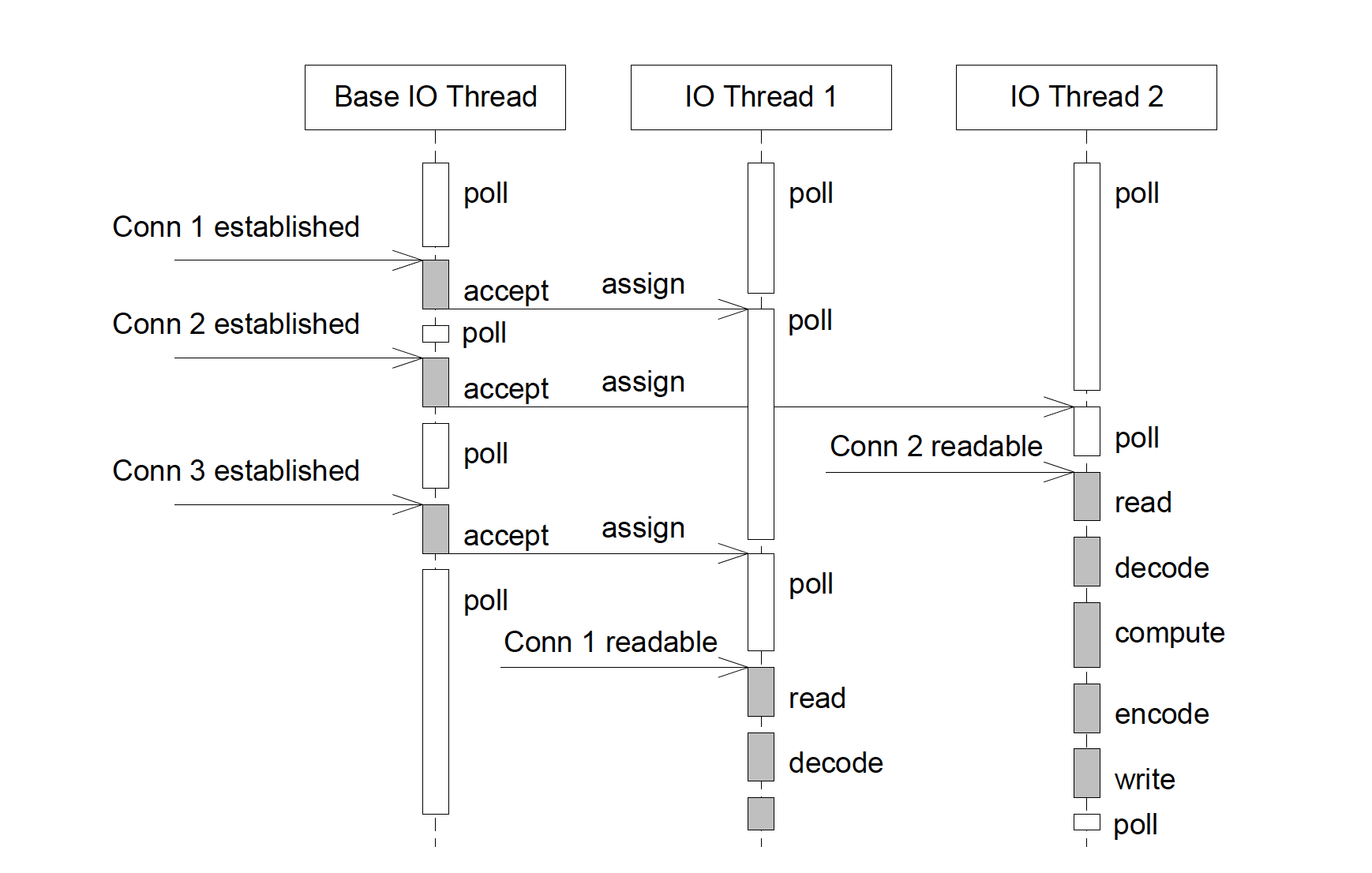
Multiple Reactors + Goroutine Pool
You may ask me a question: what if my business logic in EventHandler.OnTraffic contains some blocking code which leads to blocking in event-loop of gnet, what is the solution for this kind of situation?
As you know, there is a most important tenet when writing code under gnet: you should never block the event-loop goroutine in the EventHandler.OnTraffic, which is also the most important tenet in netty, otherwise, it will result in a low throughput in your gnet server.
And the solution to that could be found in the subsequent networking model of multiple threads/goroutines in gnet: 『multiple reactors with thread/goroutine pool』which pulls you out from the blocking mire, it will construct a worker-pool with fixed capacity and put those blocking jobs in EventHandler.OnTraffic into the worker-pool to make the event-loop goroutines non-blocking.
The networking model:『multiple reactors with thread/goroutine pool』dissolves the blocking jobs by introducing a goroutine pool, as shown below:
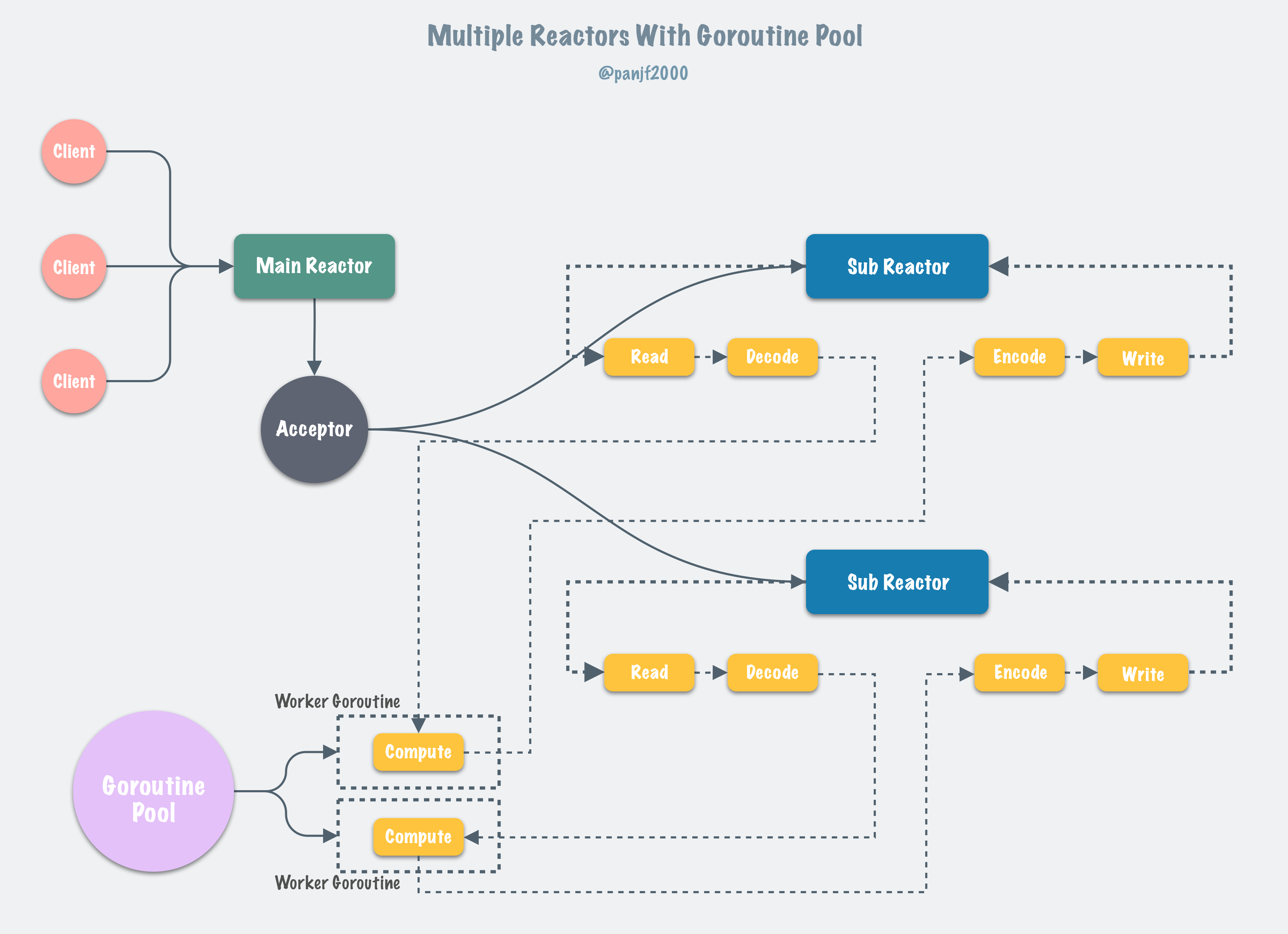
and it works as the following sequence diagram:
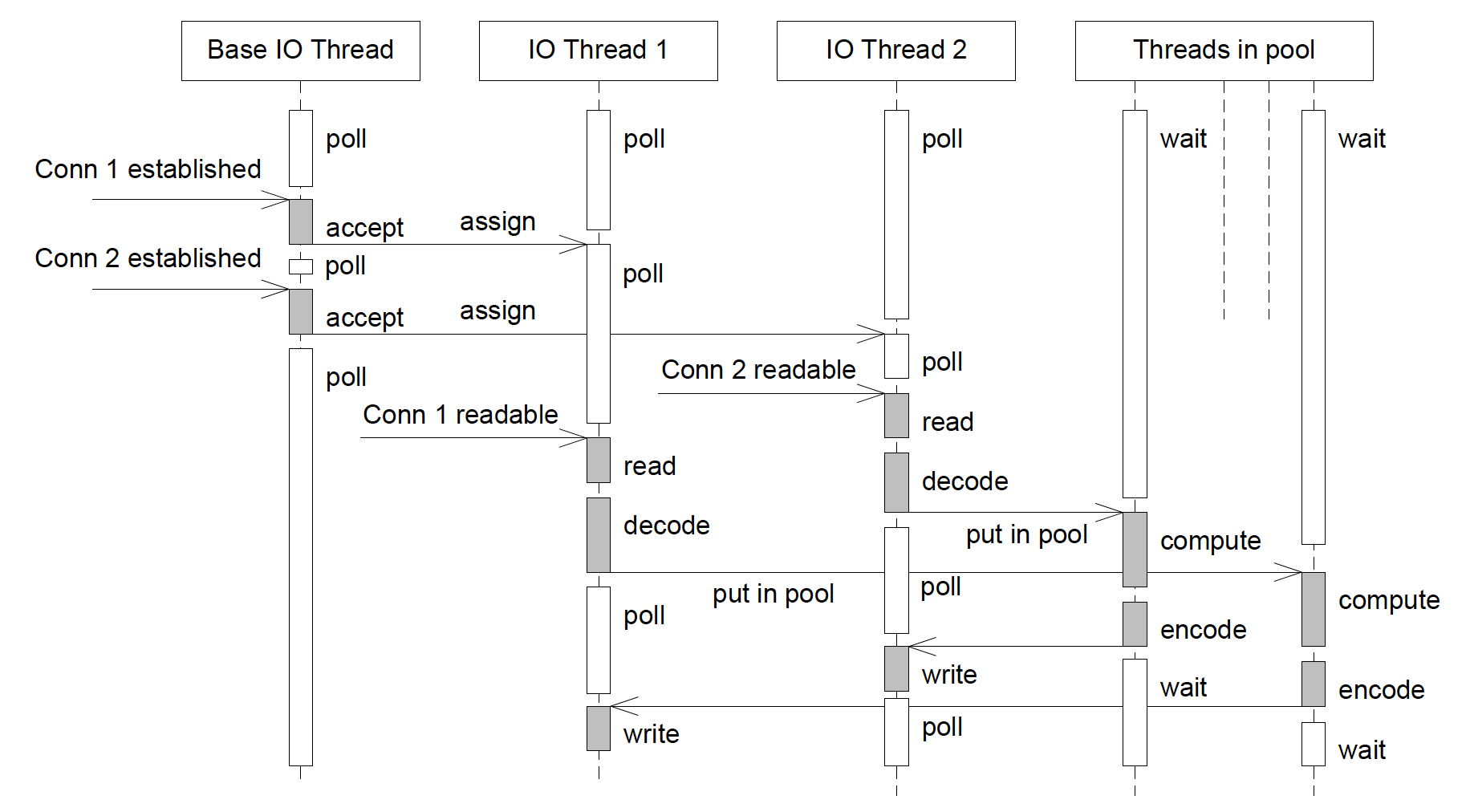
gnet implements the networking model:『multiple reactors with thread/goroutine pool』by the aid of a high-performance goroutine pool called ants that allows you to manage and recycle a massive number of goroutines in your concurrent programs, the full features and usages in ants are documented here.
gnet integrates ants and provides the pool.goroutine.Default() method that you can call to instantiate a ants pool where you are able to put your blocking code logic and call the function gnet.Conn.AsyncWrite([]byte) to send out data asynchronously after you finish the blocking process and get the output data, which makes the goroutine of event-loop non-blocking.
The details about integrating gnet with ants are shown here.
Key designs
Elastic Buffer
Elastic Ring Buffer
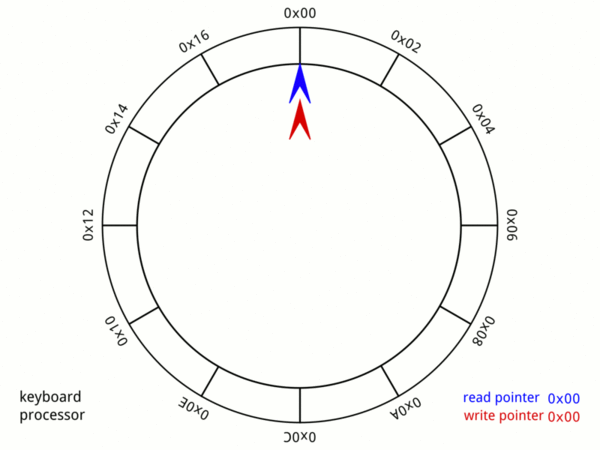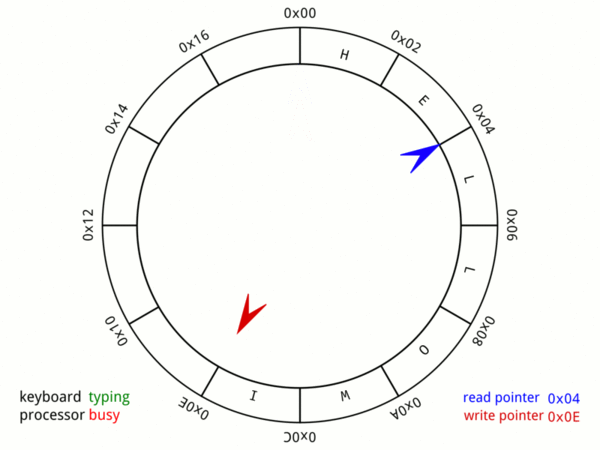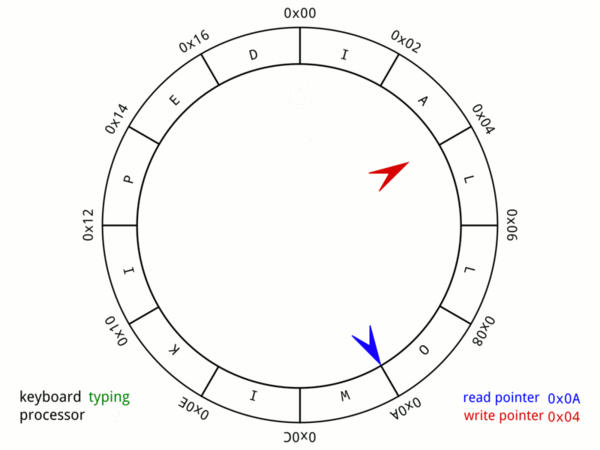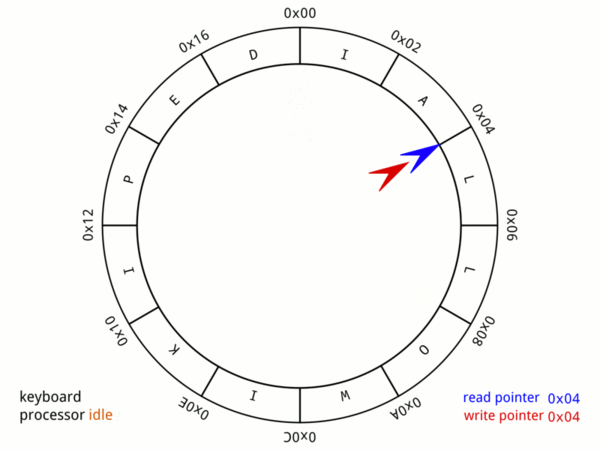
Elastic Ring & Linked-list Buffer

There are two buffers inside gnet: inbound buffer (elastic-ring-buffer) and outbound buffer (elastic-ring&linked-list-buffer) to buffer and manage inbound/outbound network data, inbound and outbound buffers inside gnet are designed and tuned to reuse memory and be auto-scaling on demand.
The purpose of implementing inbound and outbound buffers in gnet is to transfer the logic of buffering and managing network data based on application protocol upon TCP stream from business server to framework and unify the network data buffer, which minimizes the complexity of business code so that developers are able to concentrate on business logic instead of the underlying implementation.